HAND Series - Article 4 - Windows VM with GPU Passthrough

Article 4 - Windows VM with GPU Passthrough
Continuing the journey to this part is only possible when the prerequisites and Proxmox preparation is done, this parts are almost more important that the process of creation of the VM itself, because if some requirement is not met, the VM will not work as intended or not work at all.
Only if you are sure that you have done every part of the preparation you can continue with the following steps. (If you are not sure you may lose a lot of time)
The creation of the VM is done from the GUI as it is easier
- Go ahead and download the Windows ISO from the official Microsoft site
- Go ahead and download the VirtIO stable ISO from this link: https://fedorapeople.org/groups/virt/virtio-win/direct-downloads/stable-virtio/virtio-win.iso
-
Import the ISOs in Proxmox by navigating to:
- hostname → “local (hostname)” (
or the name you gave it) → ISO Images → Upload → Select the images and upload them
- hostname → “local (hostname)” (
Time to create the Windows 10 VM
- Click on Create VM on the top right
-
Steps on this part are going to be illustrated in a GIF below but just to write the important things that are done in this part :
- General → Give a Name to the VM
- OS → Select the storage where the ISO is located, then the ISO, then select Type: Microsoft Windows and below Windows 10
- Hard Disk → SCSI, choose what capacity to give it below, and some ticks in advanced are recommended, such as: SSD Emulation, IO Thread, Skip replication
- CPU → Choose as much sockets and cores as you want to give to the VM
- Memory → Choose as much RAM you want to give to the VM, is recommended to tick in advanced: Ballooning Device
- Network → Most likely your network will be vmr0, in model, choose VirtIO (paravirtualized)
- Confirm → Important to untick: Start after created
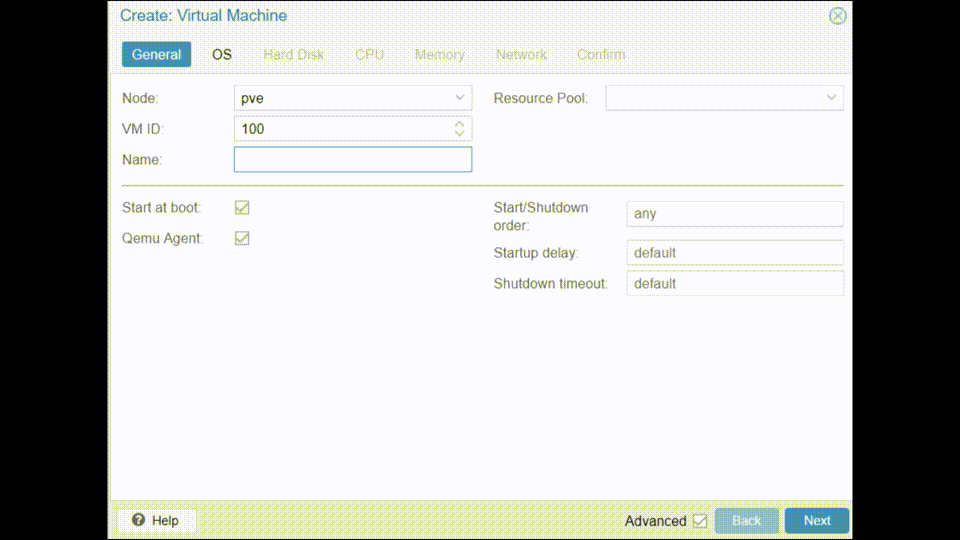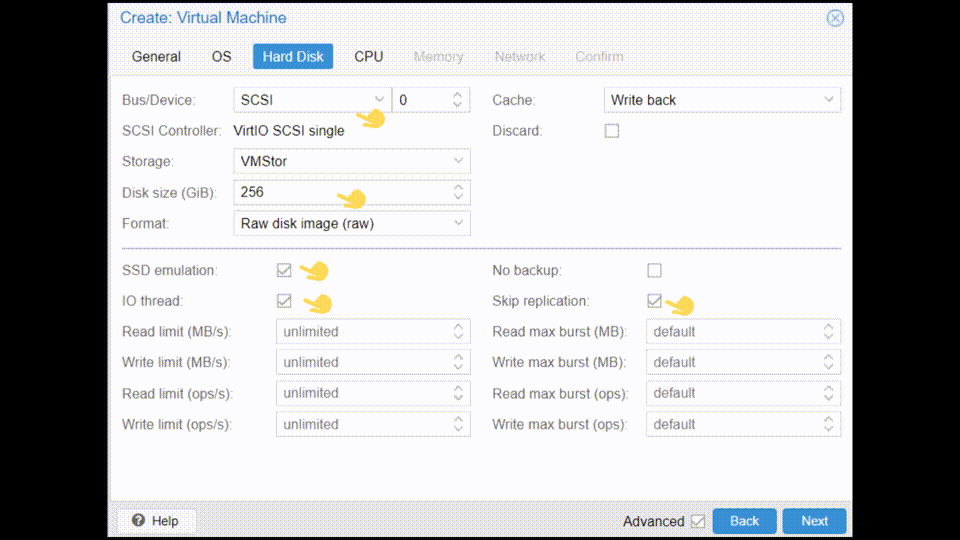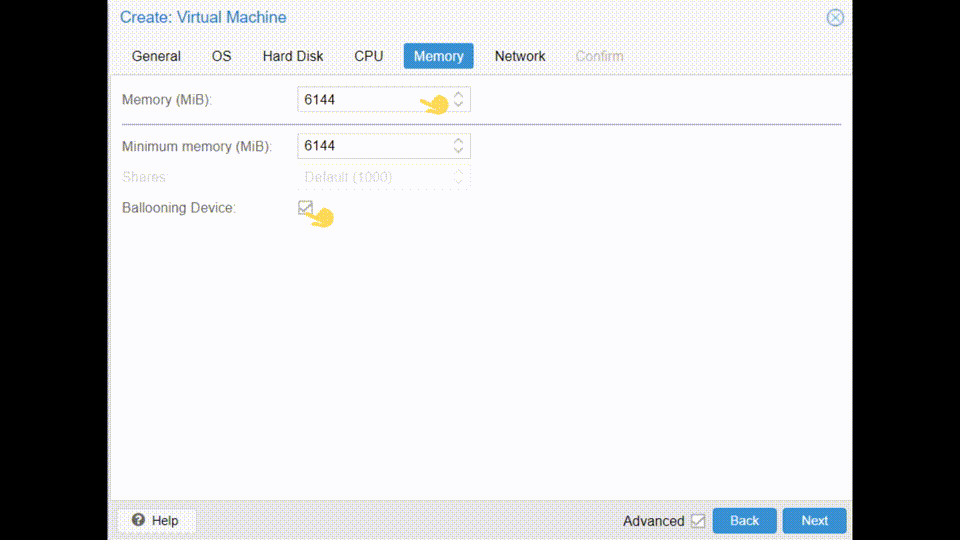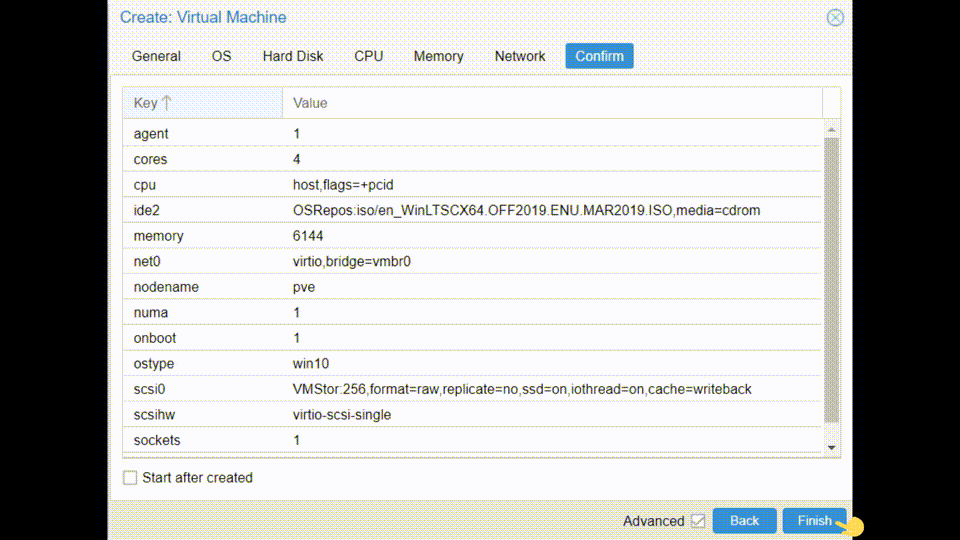
Now is very important to NOT start the VM as we will continue configuring it in the following section
-
Go to the VM Options section and set the following settings
- Boot Order → CD-ROM, Disk (scsi0)
- SCSI Controller → VirtIO SCSI Single
- BIOS → OMVF (UEFI)
-
Go to the VM Hardware section
- Add → EFI Disk. (Everything should be fine with the defaults)
Now go to the shell one more time, there are some configuration needed to be inserted directly into the VM configuration file
- Go to the shell and write (replace
with your VM ID number)
nano /etc/pve/qemu-server/<vmid>.conf- Inside, you have to add the following lines, you may paste this at the end of the file making sure you are not duplicating things, so you may delete the old parts that overlap.
machine: q35
cpu: host,hidden=1,flags=+pcid
args: -cpu 'host,+kvm_pv_unhalt,+kvm_pv_eoi,hv_vendor_id=NV43FIX,kvm=off'- Save and exit
Now go back to the VM hardware tab
- Click on ADD → PCI Device
- Select your GPU from the list
- Check on All functions
- Check on ROM-Bar
- Make sure Primary GPU is unchecked
- Check on PCI-Express
Sit tight, now is moment to START the VM
- Open the Console tab
- The Windows installation should be starting up
- On Where do you want to install Windows an error should appear as follows:
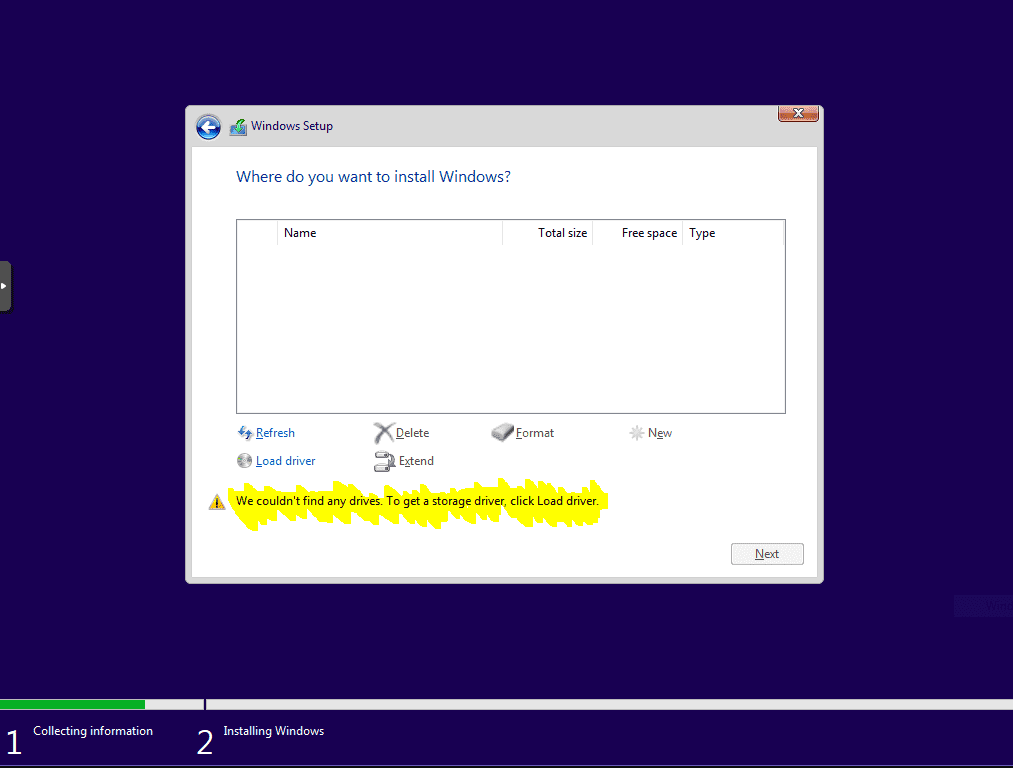
This is a process needed to be repeated a couple of times, it is the simulation of ejecting the Windows CD, putting the VirtIO drivers CD, ejecting it and putting the Windows CD again
- Being on that error state, where screen says ‘We couldn’t find any drivers…’
- Go to the hardware tab of the VM
- Click on the CD/DVD Drive → Edit
- Change the ISO to the VirtIO ISO → Save
- Go back to the installation → Click Load Driver
- Locate the drivers as follows
- Browse → CD Drive → vioscsi → win10 → amd64
- Click on Next
- After that, driver should be installed and Drive should be detected now
- Go back to hardware tab of the VM
- Click on the CD/DVD Drive → Edit
- Change the ISO to the Windows 10 ISO → Save
- Go back to the installation → Continue as usual (Follow instructions on screen, there are no more specifics to Proxmox that may give you trouble)
- After installation is done and about to restart, you may want to edit the CD/DVD Drive one more time to remove any ISO and leave it empty, this way is 100% sure it will boot on the drive with Windows, if it doesn’t, you can change the boot order on the Options tab while the VM is shut down.
What happens after the installation
-
Enable Remote Desktop
- Win Key → Write Remote Desktop → Click on Remote Desktop Settings → Toggle on
-
Install network drivers
- As usual → Go to the Hardware tab in the VM → CD/DVD Drive → Select the VirtIO ISO
- In Windows go to Device Manager → Right Click on Ethernet Controller → Update Driver
- Browse → CD Drive → NetKVM → win10 → amd64
- Ok → Next → And it should be done
-
Get the IP address
- Win + R → CMD →
ipconfig→ And note your IP address so you can connect remotely
- Win + R → CMD →
-
Remove default Console/Display
- Go to the Hardware tab of the VM
- Click on Display → Edit
- Graphic card → Select none
- Shut down the VM
-
Test the RDP Connection
- The installation of an RDP client is beyond the scope of this guide but you have RDP clients available for free for every platform (Mac, Windows and Linux)
-
Test if the GPU is there
- Open the Task Manager (
Ctrl+Shift+Esc) - Look into Performance → GPU
-
You should see the name of the GPU and the memory and stats
If you don’t see your GPU here, bad news, something along the way is not done correctly or you may need to debug further the IOMMU and why the Passthrough is not functioning as it should, you can reboot the Proxmox host and check
dmesgoutput, filter by IOMMU and debug, you have plenty of guides online, debugging this is out of the scope of the guide
- Open the Task Manager (
To be able to use the GPU on a monitor, you want to make sure the GPU and the monitor are not used by the Proxmox host, this happens during boot, so you want to make sure the HDMI cable is not hooked when Proxmox is booting, because it may show you some output and this is going to affect the Passthrough (It is a bit troublesome but is just during boot, if you have done a good job your uptime will be months without rebooting)
If you didn’t see your GPU in the Task Manager, give it a try to boot without the GPU being hooked to a monitor and connect to your Proxmox GUI from another computer, whenever you are sure the Windows VM is running hook it up, if you have your Windows screen in the monitor automatically this will tell you the GPU Passthrough is working!
At this point all it is left is to install needed Drivers, software that suits to your needs and start using the Windows 10 installation.
This is a long process, totally optional, but it is really enjoyable when it works, at the end of the day, you have a Windows installation in a VM that is completely replicable ( you can make snapshots and backups ) and reliable ( you get 99% native performance as if the installation were in bare-metal ), which is perfect for users that want to use Video Editing software or Games only available on Windows.
Also for Mac users there is the same Passthrough process that can be done to achieve the same but with Mac, if you have an additional GPU you may give it a try, but is beyond the scope of this series. (May do it in the future so stay tuned!)
Thank you for reaching this point, jump into the next article and continue your journey with me towards your dream homelab.
Thank you for being here, be healthy, happy and productive! ✌🏻